Note
Click here to download the full example code
2.2.1. Example of explicit fixed effects fMRI model fitting¶
This example illustrates how to run a fixed effects model based on pre-computed statistics. This is helpful when the initial models have to be fit separately.
For details on the data, please see:
Dehaene-Lambertz G, Dehaene S, Anton JL, Campagne A, Ciuciu P, Dehaene G, Denghien I, Jobert A, LeBihan D, Sigman M, Pallier C, Poline JB. Functional segregation of cortical language areas by sentence repetition. Hum Brain Mapp. 2006: 27:360–371. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=2653076#R11
Please see Simple example of two-session fMRI model fitting example for details. The main difference is that the fixed-effects model is run explicitly here, after GLM fitting on two sessions.
2.2.1.1. Prepare data and analysis parameters¶
Inspecting ‘data’, we note that there are two sessions
from nistats import datasets
data = datasets.fetch_fiac_first_level()
fmri_img = [data['func1'], data['func2']]
Create a mean image for plotting purpose
The design matrices were pre-computed, we simply put them in a list of DataFrames
design_files = [data['design_matrix1'], data['design_matrix2']]
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
design_matrices = [pd.DataFrame(np.load(df)['X']) for df in design_files]
2.2.1.2. GLM estimation¶
GLM specification. Note that the mask was provided in the dataset. So we use it.
from nistats.first_level_model import FirstLevelModel
fmri_glm = FirstLevelModel(mask_img=data['mask'], smoothing_fwhm=5,
minimize_memory=True)
Compute fixed effects of the two runs and compute related images For this, we first define the contrasts as we would do for a single session
n_columns = design_matrices[0].shape[1]
contrast_val = np.hstack(([-1, -1, 1, 1], np.zeros(n_columns - 4)))
Statistics for the first session
from nilearn import plotting
cut_coords = [-129, -126, 49]
contrast_id = 'DSt_minus_SSt'
fmri_glm = fmri_glm.fit(fmri_img[0], design_matrices=design_matrices[0])
summary_statistics_session1 = fmri_glm.compute_contrast(
contrast_val, output_type='all')
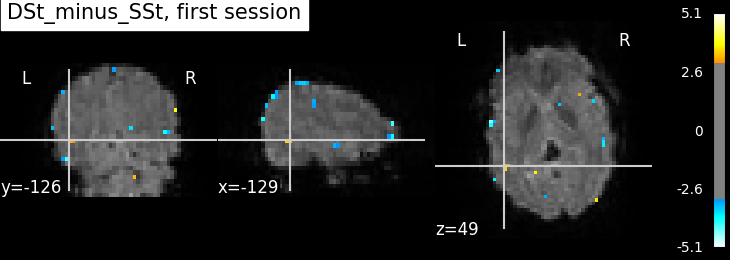
plotting.plot_stat_map(
summary_statistics_session1['z_score'],
bg_img=mean_img_, threshold=3.0, cut_coords=cut_coords,
title='{0}, first session'.format(contrast_id))
Out:
<nilearn.plotting.displays.OrthoSlicer object at 0x7f6f143d64a8>
Statistics for the second session
fmri_glm = fmri_glm.fit(fmri_img[1], design_matrices=design_matrices[1])
summary_statistics_session2 = fmri_glm.compute_contrast(
contrast_val, output_type='all')
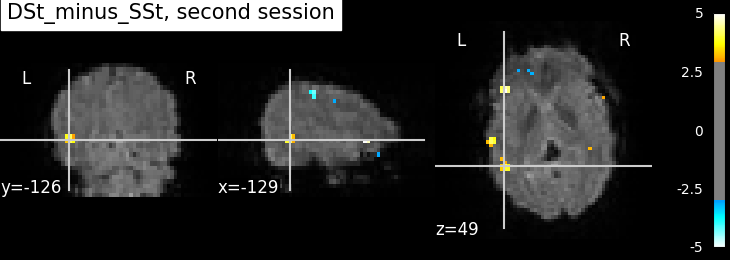
plotting.plot_stat_map(
summary_statistics_session2['z_score'],
bg_img=mean_img_, threshold=3.0, cut_coords=cut_coords,
title='{0}, second session'.format(contrast_id))
Out:
<nilearn.plotting.displays.OrthoSlicer object at 0x7f6f13d9b048>
Fixed effects statistics
from nistats.contrasts import compute_fixed_effects
contrast_imgs = [summary_statistics_session1['effect_size'],
summary_statistics_session2['effect_size']]
variance_imgs = [summary_statistics_session1['effect_variance'],
summary_statistics_session2['effect_variance']]
fixed_fx_contrast, fixed_fx_variance, fixed_fx_stat = compute_fixed_effects(
contrast_imgs, variance_imgs, data['mask'])
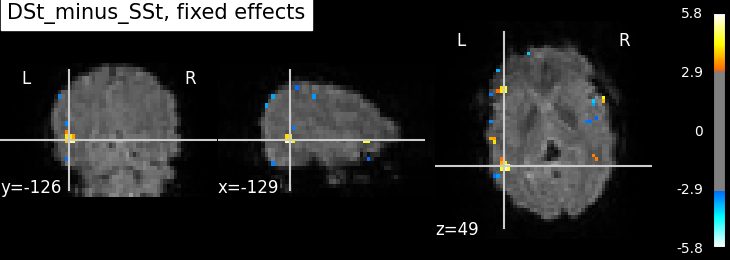
plotting.plot_stat_map(
fixed_fx_stat, bg_img=mean_img_, threshold=3.0, cut_coords=cut_coords,
title='{0}, fixed effects'.format(contrast_id))
Out:
<nilearn.plotting.displays.OrthoSlicer object at 0x7f6ec42f50f0>
Not unexpectedly, the fixed effects version displays higher peaks than the input sessions. Computing fixed effects enhances the signal-to-noise ratio of the resulting brain maps Note however that, technically, the output maps of the fixed effects map is a t statistic (not a z statistic)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 5.245 seconds)
